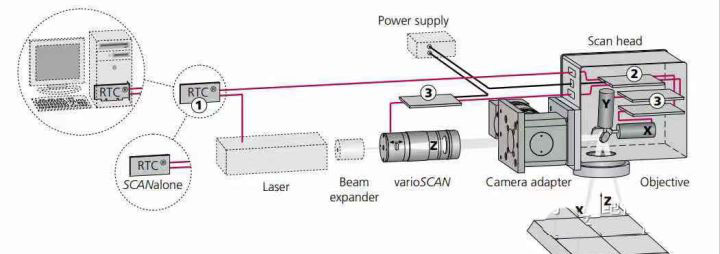
The principle of the galvanometer is: input a position signal, the swing motor (galvanometer) will swing a certain angle according to the conversion ratio of a certain voltage and an angle. The whole process adopts closed-loop feedback control, which is composed of five control circuits, such as position sensor, error amplifier, power amplifier, position discriminator, and current integrator.
A laser beam is reflected by two scanning galvanometers and passes through a focusing mirror. Driven by the motor, the galvanometer plate rotates back and forth along the axis at a high speed to achieve the purpose of changing the path of the laser beam.
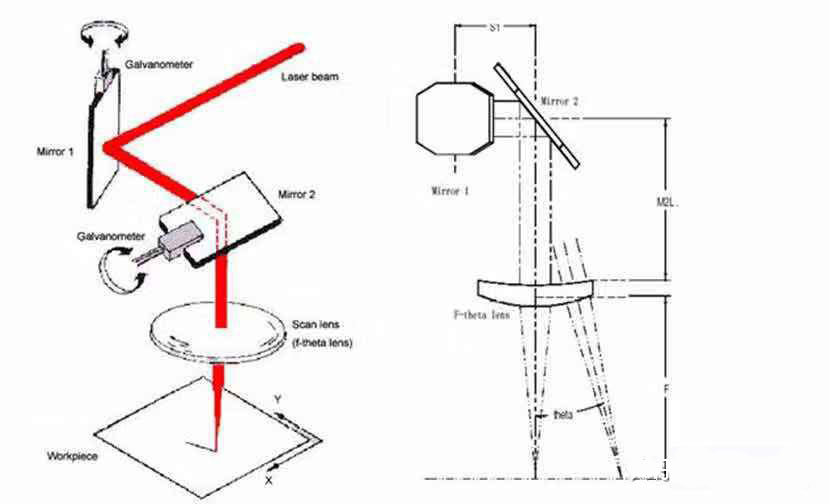
The width of lens 1 (X axis) is determined by the diameter of the beam. The width of lens 2 (Y axis) should be equal to the length of galvo mirror 1. The length of the lens 2 is the distance between the beam and S1 when the beam is on the second lens, and the maximum incident angle q.